Arrhythmia: Irregular Heartbeat That Could Lead to Heart Failure
Center : Heart Center
Article by : Dr. Patcharee Pawasuttikul

If you experience dizziness, lightheadedness, heart palpitations, or chest pain, don't consider it normal or ignore it, as these may be warning signs of "cardiac arrhythmia." This is especially important for high-risk groups with behaviors such as smoking, drinking alcohol, consuming tea or coffee, and experiencing stress, which may increase the risk of heart failure or stroke.
Table of Contents
- What is Arrhythmias?
- What are the symptoms of Arrhythmias?
- What causes Arrhythmias?
- What are the types of Arrhythmia?
- Diagnosis of Arrhythmia
- Arrhythmia Treatment
- Prevention of Arrhythmia
- Where is the best place to treat Arrhythmia?
- Get Arrhythmia treatment at Nakornthon Hospital
- Free Online Consultation with a Specialist
What is Arrhythmias?


Cardiac arrhythmia is a condition where the heart's electrical system malfunctions or short-circuits in the heart chambers, causing irregular heartbeats and reducing the efficiency of blood pumping throughout the body. Normally, the heart rate should be approximately 60-100 beats per minute, with the upper and lower chambers beating in a consistent, synchronized rhythm. However, when the heart beats irregularly—either abnormally slow (less than 60 beats per minute), abnormally fast (more than 100 beats per minute), or with occasional pauses—this indicates an arrhythmia.
What are the symptoms of Arrhythmias?
The symptoms of heart arrhythmias may vary depending on the type and severity of the irregularity. Some people may experience no symptoms at all, while others may have very clear symptoms requiring immediate treatment. Symptoms of arrhythmia include:
- Palpitations, feeling like your heart is beating strongly, rapidly, or skipping beats
- Irregular heartbeat
- Rapid heartbeat (more than 100 beats per minute)
- Slow heartbeat (less than 60 beats per minute)
- Chest pain, shortness of breath
- Tightness in the throat or epigastric area
- Dizziness, excessive sweating
- Lightheadedness, feeling faint, or loss of consciousness
- Fatigue, weakness, and lack of energy
What causes Arrhythmias?
Arrhythmias are caused by abnormalities in the heart's electrical system, resulting in the heart beating too fast, too slow, or irregularly. The causes are diverse and include:
- Smoking, drinking tea or coffee, and stress
- Chronic diseases affecting heart function such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and hyperthyroidism
- Congenital abnormalities like congenital heart muscle disorders, leaky heart valves, abnormally thick heart walls, and coronary artery disease
- Obstructive sleep apnea, which causes changes in oxygen levels and chest pressure that may lead to arrhythmias
- Certain medications including cold medicines, antihistamines, weight loss drugs, and some psychiatric medications that can have side effects causing arrhythmias
- Stress or anxiety that triggers the autonomic nervous system, causing temporary arrhythmias
What are the types of Arrhythmia?

There are no fewer than 10 types of cardiac arrhythmias, each with different mechanisms, causes, symptoms, treatment methods, and prognoses. Generally, arrhythmias can be divided into two major categories:
- Bradyarrhythmia (Too Slow Heartbeat) - Heart rate less than 60 beats per minute, including:
- Bradycardia - Heart rate slower than 60 beats per minute, resulting in insufficient blood flow to the brain and other parts of the body
- Heart Block - Electrical signal transmission from the upper to lower heart is obstructed or blocked, causing abnormally slow heartbeats, which can be fatal
- Tachyarrhythmia (Too Fast Heartbeat) - Heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute, including:
- Atrial Fibrillation - The heart beats irregularly and abnormally fast, which can cause stroke. This is commonly found, especially in elderly people, heavy alcohol drinkers, overweight individuals, and those with heart disease
- Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) - Abnormally fast heart rate exceeding 100 beats per minute, typically ranging from 150 to 250 beats per minute
- Premature Ventricular Contraction (PVC) - Occurs when the lower chambers of the heart contract before they should
- Ventricular Fibrillation - Abnormally fast and irregular heartbeat that can cause sudden loss of consciousness and death if not treated promptly. This form is less common

Diagnosis of Arrhythmia
To determine whether you have an arrhythmia, doctors will diagnose based on your symptoms, medical history, and physical examination to check the initial rhythm of your heartbeat. They may also conduct tests to identify factors that trigger arrhythmias. Doctors may use additional medical technology screening approaches, including:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) - Detects electrical currents from the heart or checks for abnormalities in the heart's electrical waves occurring in the heart muscle
- 24-hour Holter Monitor - A portable ECG device worn for 24 hours that allows doctors to detect heart rhythm abnormalities in detail. After 24 hours, you return to have the device removed and wait for the doctor's analysis of whether there are any abnormal heart waves
- Echocardiogram - Uses ultrasound to evaluate heart function, including heart muscle contraction, heart chamber size, blood circulation within the heart, heart valve function, and the position of blood vessels entering and exiting the heartc
- Exercise Stress Test (EST) - Checks for cardiovascular system abnormalities that aren't detectable when the body is at rest or not engaging in strenuous exercise. During exercise, the heart requires more oxygen from the blood
Arrhythmia Treatment
Normally, heart diseases are treated differently depending on the specific condition, such as bypass surgery or balloon angioplasty for those with coronary artery disease or blockage. For arrhythmia treatment, the following options are available:
1. Lifestyle changes
The initial treatment for arrhythmias involves behavioral changes, avoiding and controlling factors that cause irregular heartbeats. For patients with mild symptoms who don't yet have arrhythmias severe enough to cause heart failure or cardiac ischemia—just occasional palpitations—doctors will recommend avoiding smoking, alcohol consumption, or tea and coffee, as well as managing stress and reducing anxiety.
2. Heart rate-controlling medications
For more severe cases, medications may be needed to reduce heart rate, such as beta-blockers.
3. Medical treatment
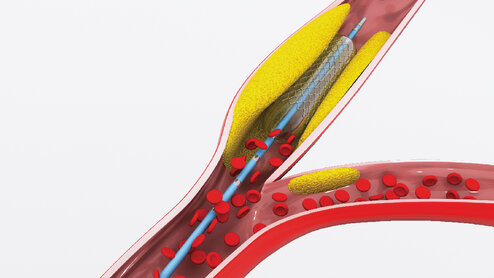
- Electrophysiologic Study and Radiofrequency Ablation: This is a non-surgical treatment for arrhythmias that doesn't require general anesthesia and isn't painful during the procedure. It's performed by inserting a catheter from the groin area to the location of the abnormal heart electrical circuit, then treating it using high-frequency sound waves that generate heat at the tip of the heart catheter. Recovery time in the hospital is just one night after the procedure, after which patients can resume normal life.
- Pacemaker Implantation: This involves implanting a device in the chest wall, under the patient's skin, to stimulate heart rhythm. The device sends electrical signals to the heart chamber that's functioning abnormally. These electrical signals help the heart beat fast enough to pump sufficient blood to the body and other organs. This treatment is used in cases where the heart rate is slower than normal.
- Automatic Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (AICD): This involves surgically implanting an automatic electric shock device for patients with severely fast arrhythmias, such as Ventricular Tachycardia or Ventricular Fibrillation.
Prevention of Arrhythmia
Arrhythmias can be prevented by managing potential risk factors through behavioral adjustments and overall health care:
- Eat nutritious food, focusing on vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and good fats. Reduce foods high in salt, saturated fats, and trans fats.
- Exercise regularly
- Maintain a standard weight
- Quit smoking, limit or avoid alcoholic beverages and caffeine
- Manage stress and get adequate sleep
- Take good care of existing conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or thyroid disease, as these conditions affect heart rhythm
- Health check-ups can help detect and manage heart disease risk factors early
Where is the best place to treat Arrhythmia?
If you experience symptoms that may indicate an irregular heartbeat, such as palpitations, chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, etc., occurring suddenly or frequently, you should see a doctor promptly.
The Heart Center at Nakornthon Hospital is ready to provide comprehensive care for all your heart health issues with a team of cardiologists and nurses experienced in specialized cardiac patient care. They have modern medical equipment, including cardiac catheterization laboratories, operating rooms, and standardized cardiac critical care units. You can be confident that patients will receive efficient treatment and care.
Get Arrhythmia treatment at Nakornthon Hospital
If you experience palpitations, dizziness, fainting or feel that your heart is beating irregularly, you should see a doctor immediately for further diagnosis, as early treatment can significantly reduce the risk of complications. The Heart Center at Nakornthon Hospital is ready to address all your heart health concerns, including diagnosis, treatment, and consultation on preventing arrhythmias, holistic health care, and managing various risk factors and lifestyle modifications to effectively reduce risks.
Nakornthon Hospital specializes in serving expatriates living in Thailand who seek fast recovery treatments with minimal hospital stays. The hospital features comprehensive, state-of-the-art medical equipment that enables efficient diagnosis and treatment of arrhythmias through advanced procedures like radiofrequency ablation, which allows patients to recover in the hospital for just one night after the procedure.
The internationally trained cardiology team is experienced in treating foreign patients, offering clear communication in multiple languages and personalized care plans that accommodate the unique needs of expatriates. Nakornthon's modern facilities and quick-recovery protocols are specifically designed for those who need to resume their normal activities promptly, making it an ideal choice for working professionals and visitors who require quality cardiac care without extended hospitalization.
For more information, please contact:
- - Website : https://en.nakornthon.com
- - Facebook : Nakornthon Hospital - International Patient
- - Line : @nakornthoninter
- - Tel: 02-450-9999 (Available 24 hours)
Free Online Consultation
Article of Heart Center


.jpg)

